BURGOYNE and his army are at Wilbur's Basin, prepared to retreat toward Lake Champlain, but lingering to pay a last sad tribute of affectionate regard to the remains of the accomplished Fraser. Night has drawn its veil over the scene, and we will turn away for a moment from the sorrowful contemplation of war and its horrid retinue, to glance at a picture lovely to the eye, ennobling to the spirit, and fruitful of pleasant impressions upon the heart and memory.
Like a "dissolving view," the smoking ruins, the sodden field, the trailing banner, the tent and breast-work and abatis, and slaughtered hundreds, and wailing families, painted in gore by the hand of human discord; and the roar of cannon, the rattle of musketry, the roll of drums, the hiss. and detonation of bombs, the savage yell, the loud huzza, the shriek and groan, the prayer and curse made audible by the boastful voice of physical strength, have all passed away with the darkness, and a bright summer's sunlight is upon the landscape. Turning the eye northward from the "American camp, there are the same gentle slopes, and deep ravines, and clustering hills, and flowing river; and the heights of Saratoga in the far distance loom up as of yore. But herds are grazing upon the lowlands, and flocks are dotting the hills; the ring of the mower's scythe is heard in the meadow, and the merry laugh goes up from the russet harvest-field, Art, with its strong arm of industry, has dug another river along the plain for the use of commerce; the forest has been reaped by agriculture, habitations of prosperity are on every hand, and the white wing of peace is spread out over all. It is a pleasant sight; therefore let us enjoy it, and, for a while, forget the dark picture of the past which we have been contemplating.
I spent nearly the whole of the day rambling and sketching upon the camp and (July 21 1848.) battlegrounds of Stillwater. It was excessively warm, although a strong breeze from the south constantly prevailed. As early as ten o'clock dark clouds began to rise in the, west, and the rumbling of distant thunder was audible. All day long, shower after shower arose threateningly, sometimes approaching so near that sharp claps of thunder would startle us; but they all swept along the horizon west and north, and disappeared behind the eastern hills. Not a drop of rain fell at Bemis's. I remarked the phenomenon, and was told that showers never reached, there from the west. Their birth-place seems to be Saratoga Lake, about six miles westward from the Hudson, and the summer rain-clouds which rise there generally pass up the lake to its outlet, the Fish Creek, and, traversing that stream until it falls into the Hudson, cross the valley and pass on to the Green Mountains, or spend their treasures upon the intervening country.
About half past three in the afternoon a canal packet arrived from the south, and we embarked for Schuylerville, nine miles above Bemis's. As usual, the boat was crowded to excess, and, the sun being veiled by the clouds in the west, the passengers covered the deck. As we passed quietly along the base of the hills whereon was Gates's camp, crossed Mill Creek or Middle Ravine, and approached Wilbur's Basin, it required but small exercise of the imagination, while listening to the constant roll of thunder beyond the heights, to realize the appalling sounds of that strife of armies which shook those hills seventy years before, as it fell upon the eager ears of wives, and sisters, and children whose cherished ones were in the midst of the storm.
Proceeding northward, we approached the track of the showers, and, just before we
70
reached Wilbur's Basin, a cloud, black as Erebus, and so low that it seemed to rest upon the hill-tops, spread out above us like the wings of a monster bird; and in its wake huge masses of vapor, wheeling like the eddies of a. whirlpool, came hastening on. The experienced boatmen understood these portents, and covering the baggage with strong canvas, lashed it tightly to the vessel. The breeze was still, and a hot, suffocating calm ensued. The passengers, warned by the helmsman, retreated into the cabin, and the windows were closed. The cattle in the fields huddled in groups, and every bird and fowl, conscious of impending danger, sought shelter. A flash of lightning, followed instantly by a crashing thunder-peal, broke over the valley, and seemed to sever the fetters of the wind. A sullen roar was heard in the distance, like the rush of great waters; the trees of the forest began to rock, and from the roads behind us clouds of dust arose and filled the air. In a few moments a tornado was upon us in its strength. It lasted only two minutes, but in its track the results of the labor of the farmer for many days were destroyed. Hay-cocks and wheat sheaves were scattered like thistle-down, and the standing grain was laid upon the earth as by the tread of a giant footstep. As the wind passed by, the rain came down gently, and continued to fall until we reached Schuylerville.
There came on the boat at Bemis's "a poor exile from Erin," with a patched coat and pair of thin pantaloons hanging over one arm. He was immediately introduced to the captain by the attentive steward, when he pleaded poverty, and declared that he hadn't a "cint in the world." He was ordered ashore, and the boat was guided accommodatingly near the bank. The poor fellow urged fatigue, and the weight of his brogans testified to the truth of the appeal, if he had walked a mile. It was cruel to doubt the honesty of that hard-favored face, and fifty cents were soon collected for him as a peace-offering to the captain. When the gust came on, he refused to go into the cabin. He had been in a three days gale upon the Atlantic, and was not to be frightened by a squall on land. The first blast of the hurricane wheeled him several times around upon deck, and came very near putting him ashore, willing or not willing. While he was endeavoring to seize a support, the wind grasped his extra pantaloons, and, in utter dismay, he saw them gyrating, like a spread eagle, high in air, and becoming "small by degrees and beautifully less" in the distance. The loss distressed him greatly-far more than the helmsman thought necessary, and he ordered him to be quiet. "Indade," said the poor fellow, "do ye think a man can be quiet when the wind is rolling him like a bag o' feathers tied fast at one end, and all he has in the world snatched from him by the blackguard gale?" and he looked agonizingly toward the point where his pantaloons had vanished.
"Precious small, estate," answered the amused helmsman, "if a pair of old pantaloons is all you have in the world. I'll give you a better pair than that if you'll stop your noise."
"An' wid three Vickeys sowed up in the waistbands?" eagerly inquired the exile.
His cautiousness was here at fault. He hadn't a "cint in the world," but he had three sovereigns sewed up in the waistbands of the pantaloons which had gone a-ballooning. As soon as the gale passed by, a child of the Green Isle was a foot-passenger upon the towpath, bearing sorrowful testimony to the truth of the ethical maxim, that retributive justice is always swift to punish offenders against truth and honesty. No doubt his thoughts were all with his absconded sub-treasurer, and the prose of Holmes's poem evidently engrossed his mind:
"I saw them straddling through the air,
Alas! too late to win them;
I saw them chase the clouds as if
The devil had been in them.
They were my darlings and my pride,
They carried all my riches:
'Farewell, farewell!' I faintly cried,
'My breeches! O my breeches !' "
It was about four o clock when we passed the burial-place of General Fraser. It had been my intention to stop there for an hour, and visit the last earth-home of the illustrious
71
dead. But the rain fell fast, and the day was so far consumed that I was obliged to forego the melancholy pleasure. The canal is so near the base of the hill, that I easily made the sketch of it (printed on page 67) from the cabin-window. Many years ago a distant relative of the general proposed to remove his remains to Scotland, and lay them beside those of his mother; but they are still undisturbed where his sorrowing comrades laid them.
We reached the little settlement of Coveville at half past four, the rain still falling gently. This was formerly Do-ve-gat, or Van Vechten's Cove, as it was sometimes called, the place where the British tarried from the 15th till the 17th of September, while a working party repaired the roads and bridges in advance to Wilbur's Basin. Here was the (1777.) residence of Colonel Van Vechten, of the Saratoga militia, one of General Gates's staff. He was a zealous Whig, and the active Tories, whose plans his vigilance often frustrated, were greatly imbittered against him politically, while they honored him as a brave man and good neighbor.(1) Burgoyne, on his retreat to Saratoga after the battle of the 7th of October, ordered the dwellings of several Whigs to be destroyed; and at Do-ve-gat the buildings 1777. of Colonel Van Vechten were the first to which the torch of the invader was laid. His family fled to Albany on the approach of Burgoyne from Fort Edward; and when they returned, late in October, their fine estate was a perfect wreck, and they had no shelter for their heads.
Colonel Van Vechten was at Albany, on public business, at the time of the first battle on Bemis's Heights. He had received an order from the Committee of Safety at that city, when Burgoyne marched from Fort Edward, to remove every Tory or disaffected person from his vicinage into Connecticut. This order touched his excellent heart with grief, for many of those included in the proscription were his neighbors, and some were his personal friends, who honestly differed from him in relation to the momentous political questions at issue. Within six hours after receiving the order he was in Albany, and procured its recall. The humanity, policy, and sound wisdom of that step were soon illustrated by the firm support which some of these disaffected ones gave to the American cause.
We landed at Schuylerville in the midst of "sun and shower," for the sky was clear in the west, yet the rain-drops came glittering down profusely. The Fish Creek, which here has a succession of falls and rapids for nearly a mile, affording fine water-power for several mills, was brimful with the showers of the day, and poured its flood, roaring and foaming, under the canal viaduct with such force as to shake the solid masonry. It empties its waters into the Hudson about one hundred rods east of the canal, at the southeast angle of Old Fort Hardy, now among the buried things of the past. Upon the plain north of thc creek, near the old fort, the forces of Burgoyne laid down their arms; and on every side of that pleasant village scenes of historic interest lie scattered. The earth was too wet to invite a sunset ramble, and we contented ourselves with viewing the beauty of the scene that spread out before us eastward while loitering upon the upper piazza of the Schuylerville House.
1 I have already had occasion to use the terms Whig and Tory, and shall do so often in the course of this work. They were copied by us from the political vocabulary of Great Britain, and were first used here, to distinguish the opposing parties in the Revolution, about 1770. The term originated during the reign of Charles II., or about that time. Bishop Burnet, in his History of his own Times, gives the following explanation: "The southwest counties of Scotland have seldom corn enough to serve them round the year: and the northern parts producing more than they need, those in the west come in the summer to buy at Leith the stores that come from the north; and, from a word, whiggam, used in driving their horses, all that drove were called whiggamores, and shorter, whiggs. Now in that year, after the news came down of Duke Hamilton's defeat, the ministers animated their people to rise and march to Edinburgh, and then came up marching at the head of their parishes, with unheard-of fury, praying and preaching all the way as they came. The Marquis of Argyle and his party came and headed them, they being about six thousand. This was called the Whiggamore's inroad, and ever after that all that opposed the courts came, in contempt, to be called Whigg; and from Scotland the word was brought into England, where it is now one of our unhappy terms of distinction." Subsequently all whose party bias was democratic were called Whigs. The origin of thc word Tory is not so well attested. The Irish malcontents, half robbers and half insurgents, who harassed the English in Ireland at the time of the massacre in 1640, were the first to whom this epithet was applied. It was also applied to the court party as a term of reproach.-See, also. Macaulay's History of England, i., 240.
72
It was, indeed, a charming scene, enhanced by the associations of the vicinity. The face of nature was washed clean by the drenching showers; the trees and shrubs were brilliant green; and from the clustering knolls or loftier hills beyond the Hudson, once bristling with bayonets or wreathed by the smoke of cannon, the evening sunlight was reflected back by the myriad rain-drops lying upon trees, and grass, and blooming com. Nor was this all. Upon the dark background of the hills was Iris,
" That beautiful one,
Whose arch is refraction, whose keystone the sun;
In the hues of its grandeur sublimely it stood
O'er the river, the village, the field, and the wood."
CHARLES SWAIN.
Springing from the plain, its double arch spanned the whole ground where British pride was humbled and American valor acknowledged. I never gazed upon the" bow of promise" with so much interest, for thought unconsciously bridged over the chasm of seventy buried years, and it seemed for a moment as if the dark hours of our rebellious conflict had returned, and that in the covenant seal before me the eye of hope read prophetically the history of the happy present. As the sun went down and the bow faded, the Spirit of Beauty left traces of its pencil on my thoughts, and I felt, with "AMELIA," that
"There are moments, bright moments, when the spirit
receives
Whole volumes of thought on its unwritten leaves,
When the folds of the heart in a moment unclose,
Like the innermost leaves from the heart of the rose;
And thus, when the rainbow had passed from the sky,
The thoughts it awoke were too deep to pass by;
It left my full soul like the wings of a dove,
All flutt'ring with pleasure, and flutt'ring with love."
In the evening I visited the son of Colonel Van Vechten just named, a man of three score and ten years. His memory is unclouded, and extends back to the closing scenes of the Revolution. His father stored that memory with the verbal history of his times, and every noteworthy locality of Saratoga is as familiar to him as the flower-beds of his beautiful garden. He kindly offered to be my guide in the morning to all the places here made memorable by the events connected with the surrender of Burgoyne.
While awaiting the dawn, let us turn to the past, and view occurrences from the burial of Fraser to the closing scenes of the drama.
(October, 1777.) As soon as the funeral ceremonies at Fraser's burial were ended on the evening of the 8th, Burgoyne, fearing that the Americans (whose forces constantly increased, and whose activity denoted preparations for some bold movement) might succeed in turning his right and surrounding him, commenced a night march toward Saratoga. A retreat was anticipated by General Gates, and, previous to the action on the 7th, he sent General Fellows with a detachment of fourteen hundred men to occupy the high grounds east of the Hudson, opposite the Saratoga ford, intending, in case the enemy retreated, to follow so closely in pursuit as to be able to re-enforce that officer from the ranks of the main army. He also sent another detachment, after the action, to occupy ground higher up near Fort Miller, and ordered a selected corps of two thousand men to push forward and occupy the heights beyond Saratoga, in the direction of Lake George. But the retreat of Burgoyne was at a time when Gates least expected it. The troops of the former had been in motion all the night before, and under arms all day on the 8th, and he supposed that they would tarry for rest until the morning of the 9th.
At sunset on the 8th a lurid haziness in the west indicated an approaching storm, and before midnight the rain began to fall. The enemy felt that his situation was too perilous to be maintained, and the whole British army commenced its march at nine o'clock in the evening. The loss of Fraser was now severely felt, for he had always showed as consummate skill in managing a retreat as bravery in leading to an attack. General Riedesel
73
commanded the van-guard and General Phillips the rear-guard. The night was so dark, the rain so incessant in the morning, and the roads were so bad, that the royal army did not reach Saratoga until the evening of the 9th. They made a halt about six o'clock in the morning, and General Riedesel, exhausted by fatigue, went into the caleche in which his wife and children were, and slept soundly for about three hours. Wet and weary, and harassed by the Americans all the way, the poor soldiers were too much exhausted even to cut wood for fires, and they lay down upon the cold, wet ground and slept. The generals reposed in the open air, upon mattresses, with no other covering than oil-cloth. The Baroness Reidesel and other women of the British camp were obliged to submit to these privations. "My dress," the former says, "was wet through and through with rain, and in this state I had to remain the whole night, having no place to change it; I, however, got close to a large fire, and at last lay down on some straw. At this moment General Phillips came up to me, and I asked him why he had not continued our retreat, as my husband had promised to cover it and bring the army through. 'Poor dear woman,' he said, 'I wonder how, drenched as you are, you have the courage still to persevere, and venture further in this kind of weather. I wish,' he continued, 'you were our commanding general; General Burgoyne is tired, and means to halt here to-night and give us our supper.' "(1) No doubt there was more sincerity than compliment in General Phillips's wish, for the frequent halts and great delays of Burgoyne had dissatisfied his officers, and were, doubtless, chief causes of his misfortunes. His ambition and his love of ease were often wrestling, and the latter too frequently gained the mastery.
The retreat of Burgoyne was so sudden, that he left all his sick and wounded in the hospital behind him, together with a great number of wheel carriages and other things collected at Wilbur's Basin. The invalids, amounting to about three hundred, were treated by General Gates with the utmost humanity, which Burgoyne afterward gratefully acknowledged. On retiring, the English burned the houses they had occupied, and many other things which they could not carry away with them. They also wantonly set fire to several buildings on the way, by order of Burgoyne himself; and among others, when they crossed the Fish Creek, the mansion of General Schuyler, his mills and other property, amounting in value to twenty thousand dollars, were destroyed by them.
The house of General Schuyler was elegant for the times, and was very
pleasantly situated  upon
the south bank of the Fish Kill or Fish Creek. It was rebuilt after the
war but in a style much inferior in beauty and expense. It is still standing,
and in the present possession of George Strover, Esq. The broad lawn in
front is beautifully shaded with venerable trees; and the falls of the Fish
Creek close by contribute, by their music and wild beauty, much to the interest
of the scene. The mill was also rebuilt in the same style. In the engraving
is given a correct representation of it. Many of the logs in the dam are
the same that curbed the stream in the time of the Revolution; and I was
told that little was wanted to make the whole appear as at that period,
but that the surrounding hills should be covered with dense woods.
upon
the south bank of the Fish Kill or Fish Creek. It was rebuilt after the
war but in a style much inferior in beauty and expense. It is still standing,
and in the present possession of George Strover, Esq. The broad lawn in
front is beautifully shaded with venerable trees; and the falls of the Fish
Creek close by contribute, by their music and wild beauty, much to the interest
of the scene. The mill was also rebuilt in the same style. In the engraving
is given a correct representation of it. Many of the logs in the dam are
the same that curbed the stream in the time of the Revolution; and I was
told that little was wanted to make the whole appear as at that period,
but that the surrounding hills should be covered with dense woods.
The rain was so heavy on the 9th, that General Gates did not commence his pursuit until nearly noon on the tenth. The
1 Letters of the Baroness Riedesel.
74
detachment under Fellows was unconsciously in a perilous situation for
want of re-enforcements.  Resting
in supposed security on the night of the 9th, his camp was left so entirely
unguarded that an officer, who had been sent forward by Burgoyne to reconnoiter,
marched all around it without meeting a sentinel! This neglect would have
been fatal if Burgoyne had known the exact position of his enemies around
him. The officer urged him to allow him to surprise Fellows, but misfortune
had made the British general wary and suspicious, and, fortunately for the
Americans, the request was denied.
Resting
in supposed security on the night of the 9th, his camp was left so entirely
unguarded that an officer, who had been sent forward by Burgoyne to reconnoiter,
marched all around it without meeting a sentinel! This neglect would have
been fatal if Burgoyne had known the exact position of his enemies around
him. The officer urged him to allow him to surprise Fellows, but misfortune
had made the British general wary and suspicious, and, fortunately for the
Americans, the request was denied.
The main army of Gates reached the high ridge between Saratoga Church and the Fish Creek at about four in the afternoon of the 10th. The British had crossed over the creek, and were encamped upon the high grounds on the slope of which Schuylerville is now built.(1) The two armies were within the sound of each other's music. The boats of Burgoyne, with his baggage and provisions, were at the mouth of the creek. A fatigue party began to carry the stores from the boats to the heights, but Fellows constantly played upon them with two field pieces stationed on the flats beyond the river, and they were obliged to retreat to the camp. Several of the bateaux of the enemy, with their provisions, were captured, and immediately became objects of plunder for the raw militia and motley followers of the army. Even the Continental troops were implicated in taking" pay and rations" for servo ices, directly from the enemy, instead of receiving them through the paymaster. These irregularities became so extensive that General Gates issued an order on the 12th, in which he declared that he "saw so many scandalous and mean transactions committed by persons who sought more after plunder than the honor of doing their duty, that it was his unalterable resolution to have the first person who should thereafter be detected in pillaging the baggage and stores taken from the enemy, tried and punished with the utmost severity of the military law."(2)
Finding the ford across the Hudson strongly guarded by the Americans, Burgoyne resolved to continue his retreat up the right bank of the river to the front of Fort Edward, force his way across, and take possession of that fortress. He sent forward a working party, consisting chiefly of loyalists, guarded by Fraser's marksmen, to repair the bridges and open the roads, and also a detachment of troops to take possession of the fort. The Americans, who were spreading out in small detachments upon every height, on all sides, soon drove the workmen back into the camp; and the British troops found the fort in the possession of two hundred Americans, under Colonel Cochrane. The militia were flocking to the fort to strengthen the garrison, and the enemy, believing the Americans to be as numerous in front as in rear, hastily retreated back to their lines.
1 The village of Schuylerville is on the north bank of the
Fish Creek. Old Saratoga, with its church, was on the south side. The church
was about eight hundred yards south of the creek, on the road to Albany.
2 It is said that when Burgoyne proposed in. council, on the 13th, to retreat
precipitately, he mildly reproached Major Skene, a stanch loyalist, with
having brought him into this difficulty by injudicious advice, particularly
with regard to the expedition to Bennington. "You have brought me into
this difficulty," he said; "now advise me how to get out of it."
"Scatter your baggage, stores, and every thing else that can be spared,
at proper distances," replied the major, "and the militia will
be so engaged in collecting and securing the same, that the troops will
have an opportunity of getting clear off."
3 (Couldn't find where the 3 was in the above text, ajb) The two victories
on Bemis's Heights greatly inspirited the Americans, and when, after the
last battle, General Gates, in order to make victory secure, applied to
the Legislature of New Hampshire for more troops, the militia turned out
with alacrity. The speaker of the Assembly, John Langdon, Esq., upon receiving
the application, immediately proposed an adjournment, and that as many members
as could should set off directly as volunteers for the cause, taking with
them all the men they could collect. It was agreed to, and done by himself
and others.-Gordon, ii., 262.
75
Thus the cloud of perils thickened around Burgoyne. He now abandoned all idea of saving his artillery and baggage, and saw no other mode of escape than a precipitate retreat. The provisions and other stores in his bateaux were captured or destroyed by the republicans, and from every direction he was galled by a desultory fire from cannon and small arms. So overwhelming was the number of the Americans, that to fight would be madness, and Burgoyne lost all hope of saving his doomed army.
But in the midst of all these perils and despondencies, a stratagem of the British commander, suggested by an erring apprehension on the part of General Gates, aided by the occurrence of a natural phenomenon, came very near being successful, and for a time greatly cheered the drooping spirits of the enemy. Rumor reached General Gates that the whole British army had moved toward Fort Edward, leaving only a small detachment, as a rearguard, in defense of the camp. This rumor originated from the march of the detachment already mentioned, which was sent forward to Fort Edward. General Gates, therefore, determined to cross the Fish Creek on the morning of the 11th, fall in full force upon and crush the British rear-guard, and make a vigorous pursuit after the main body.
By some means this determination of Gates's became known to Burgoyne, and he resolved to profit by the false rumor. He left a strong guard at the battery on the creek, and concealed his troops in the thicket, a few rods in the rear. In the morning the sky was cloudless, but a thick fog rested upon the whole country and obscured every object. This was hailed as a favorable event by both generals, Gates supposing that it would veil his movements from the British rear-guard, and Burgoyne confidently believing that it would conceal his ambush, and that victory was now certain.
The brigades of Generals Nixon and Glover, and Morgan's corps, were ordered
to cross the creek and fall upon the enemy's camp. Morgan advanced at about
daylight, the fog being so thick that he could see but a few rods around
him. He at once fell in with the British pickets, who poured in a volley
upon him and killed a lieutenant and several privates. Morgan instantly
conceived that the rumor was false, and that the enemy was in force near.
At that moment Deputy Adjutant-general Wilkinson, who had been sent by Gates
to reconnoiter, rode up, and, coinciding in opinion with Morgan, hastened
to report to his commander the supposed peril of his corps. The brigades
of Patterson and Learned were immediately dispatched to its support. Nixon
and Glover were at the  same
time pressing forward to attack the camp, while the whole army advanced
to the heights immediately south of the creek. Nixon crossed the creek to
the plain, and surprised a picket guard at Fort Hardy; and Glover was about
to follow him, when a British soldier was seen hastily fording the stream.
He was captured, and professed to be a deserter. Glover questioned him,
and was informed that the entire British army were in their camp, drawn
up in order of battle. The general suspected him of untruth, and threatened
him with instant death if he should deceive him. The soldier declared that
he was an honest deserter, and solemnly affirmed the truth of his tale,
which was soon confirmed by a German deserter, and by the capture of a reconnoitering
party, consisting of a subaltern and thirty-five men, by the advance guard,
under Captain Goodale, of Putnam's regiment. The deserter was immediately
sent with one of Glover's aids to General Gates, and information was forwarded
to General Nixon, with urgent advice to halt. Satisfied of the deserter's
truth, Gates revoked all the orders of the evening previous, and directed
the troops to return to their respective positions. His headquarters were
nearly a mile in the rear of his army, and his order came almost too late
to save the troops, who had
same
time pressing forward to attack the camp, while the whole army advanced
to the heights immediately south of the creek. Nixon crossed the creek to
the plain, and surprised a picket guard at Fort Hardy; and Glover was about
to follow him, when a British soldier was seen hastily fording the stream.
He was captured, and professed to be a deserter. Glover questioned him,
and was informed that the entire British army were in their camp, drawn
up in order of battle. The general suspected him of untruth, and threatened
him with instant death if he should deceive him. The soldier declared that
he was an honest deserter, and solemnly affirmed the truth of his tale,
which was soon confirmed by a German deserter, and by the capture of a reconnoitering
party, consisting of a subaltern and thirty-five men, by the advance guard,
under Captain Goodale, of Putnam's regiment. The deserter was immediately
sent with one of Glover's aids to General Gates, and information was forwarded
to General Nixon, with urgent advice to halt. Satisfied of the deserter's
truth, Gates revoked all the orders of the evening previous, and directed
the troops to return to their respective positions. His headquarters were
nearly a mile in the rear of his army, and his order came almost too late
to save the troops, who had
1 This house is still standing. The view is taken from the road, a few rods southwest of the building. (Continued on next page.)
76
already crossed the creek, from destruction, for the fog soon passed away and discovered them to the enemy, then in full view, and under arms upon the heights. Nixon, however, had retreated, and the cannonade opened upon him by the British took effect only upon the rear of his brigade. (1)
General Learned, in the mean while, with his own and Patterson's brigades, had reached Morgan's corps, and was pressing on rapidly to the attack when Wilkinson came up, not with a counter order from Gates, but with the intelligence that the right wing of the Americans had given way. The brave veteran disliked the idea of retreating, preferring to carry out the standing order of the previous day to the very letter;(2) but, on counseling with Colonels Brooks and Tupper, and some other officers, a retreat was deemed advisable. As they turned, the British, who were awaiting an attack, opened a fire upon them; but the Americans were soon masked by the woods, and Morgan took post upon the flank and rear of the enemy.
Thus, by the providential circumstance of a deserter flying to our camp, our army was saved from a terrible, perhaps fatal, loss; for, had the several brigades of Nixon, Glover, Learned, and Patterson been cut off, Burgoyne might have so much weakened the American army, and strengthened his own by the adherence of the now wavering loyalists and Indians, as to scatter the remainder of the Continental forces and reach Albany, the darling object of all his efforts. But the breath of the deserter blasted all his hopes, and the incident was, to use his own words, "one of the most adverse strokes of fortune during the campaign."(3)
Burgoyne now saw no way of escape. He sent out scouts toward the north, who reported the roads impassable and the woods swarming with republicans. The few Indians who had remained now left him, utterly disheartened; and the loyalists, feeling that their personal security would be jeoparded in case of a surrender, left the army every hour. It was proposed to make a scattered retreat, each soldier carrying in his knapsack provisions enough for two or three days, Fort George being the place of rendezvous; but such a step would be perilous in the extreme, for the Americans, apparently as numerous as the leaves upon the trees, and ever on the alert, would cut them off in detail. In battle, a fortunate circumstance might occur in their favor; but General Gates, assured that he had his enemy in his power, could not be induced to jeopard the lives of his troops by an engagement. Burgoyne's only hope rested upon aid from Clinton below. Not a word, however, could he get from that general; yet, clinging with desperation to every hope, however feeble, he resolved to await that succor quietly in his strong camp as long as his exhausted stores and a powerful enemy would allow.
Burgoyne's camp, upon the heights near the Fish Creek, was fortified, and, extending more than half a mile in the rear, was strengthened by artillery. On an elevated plain, northwest of the village of Schuylerville, his heavy guns were chiefly posted. Directly in his rear Morgan and his corps were stationed. In front, on the east side of the Hudson,
It is of wood, and has been somewhat enlarged since the
Revolution. It was used by General Gates for his quarters from the 10th
of October until after the surrender of Burgoyne on the 17th. It belonged
to a Widow Kershaw, and General Gates amply compensated her for all he had.
on leaving it. It is now well preserved. It stands on the east side of the
Albany and Whitehall turnpike, about a mile and a half south of the Fish
Creek. The Champlain Canal passes immediately in the rear of it; and nearly
half a mile eastward is the Hudson River.
1 John Nixon was born at Framingham, Massachusetts, March 4th, 1725. He
was at the siege of Louisburg in 1745, was captain in the provincial troops
under Abercrombie at Ticonderoga, and was esteemed a valiant soldier during
the whole of the French and Indian war. He took the patriot side when our
Revolution broke out. He was one of the minute men at the Lexington battle,
was at the head of a regiment in the battle of Bunker Hill, and was made
a brigadier in the Continental army in August, 1776, He was then placed
in command at Governor's Island, near New York. In the battle of Bemis's
Heights a cannon-ball passed so near his he.ad it impaired the sight of
one eye and the hearing of one ear. On account of ill health, he resigned
his commission in 1780. He died March 24th, 1815, aged 90 years.
2 The standing order was, "In case of an attack against any point,
whether front, flank, or rear, the troops are to fall on the enemy at all
quarters."
3 Letter to Lord George Germain, dated Albany 20th, 1777.
77
Fellows, with three thousand troops, was strongly intrenched. The main body of the American army, under Gates, was on the south side of the Fish Creek; and in every direction small detachments of Continentals or republican militia were vigorously watching the enemy at bay.(1) Fort Edward was in possession of the Americans, and upon high ground in the vicinity of Glenn's Falls they had a fortified camp.
Burgoyne was completely environed, and every part of the royal camp was exposed to the fire of cannon and musketry. The soldiers slept under arms continually. There was not a place of safety for the sick, wounded, and dying, or for the women and children of the officers and soldiers. There was no secure place for a council. None dared go to the river for water, and thirst began to distress the camp.(2) The desertions of the Indians and Canadians, the cowardice and disaffection of the loyalists, and the losses in killed and wounded, had so thinned Burgoyne's ranks, that his army was reduced one half, and a large proportion of those who remained were not Englishmen. There was not bread for three days in store, and of course none could be obtained. Not a word came from General Clinton, and Burgoyne was totally ignorant of his having made any movement up the Hudson. The last ray of hope faded away, and toward the evening of the 12th the British commander held a council with Generals Reidesel, Phillips, and Hamilton. It was decided to retreat before morning, if possible; but returning scouts brought only hopeless intelligence respecting the roads and the strength of the enemy.
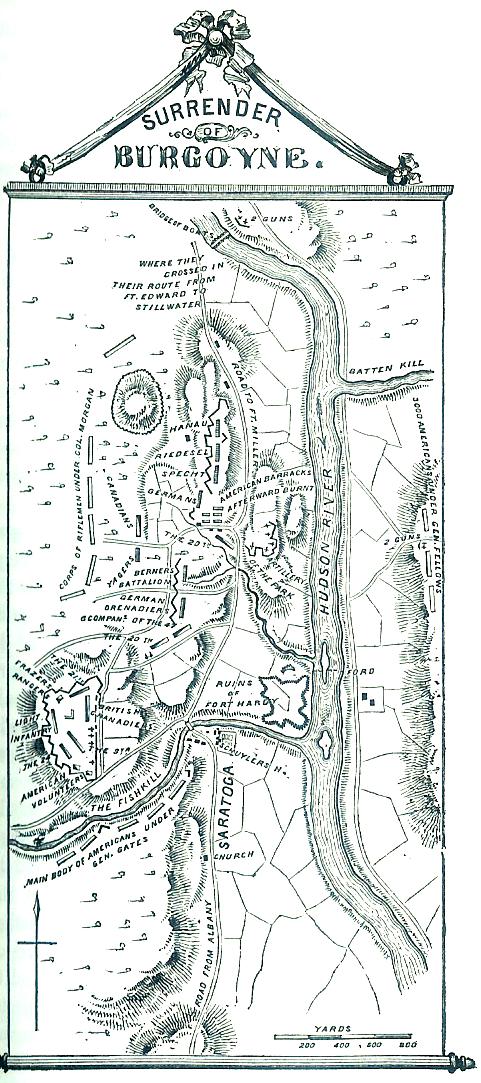
On the morning of the 13th Burgoyne called a general council of all officers, including captains of companies. Their deliberations were held in a large tent, which was several times perforated by musket. balls from the Americans. Several grapeshot struck near the tent, and an eighteen pound cannon-ball swept across the table at which sat Burgoyne and the other generals. Their deliberations were short, as might be expected, and it was unanimously resolved to open a treaty with General Gates for an honorable surrender. It was a bitter pill for the proud lieutenant general, but there was no alternative.
1 By reference to the above map, the position of the two
armies at this juncture will be more clearly understood. They held the same
relative position until the surrender on the 17th.
2 The consideration of Americans for women was conspicuously displayed at
this time. While every man who went to the river for water became a target
for the sure marksmen of the Americans, a soldier's wife went back and forth
as often as she pleased, and not a gun was pointed at her.
78
Toward evening a flag was sent to General Gates, with a note, intimating that General Burgoyne was desirous of sending a field officer to him upon a matter of great moment to both armies, and wishing to know at what hour the next morning it would suit General Gates to receive him. The reply was, "At ten o'clock, at the advanced post of the army of the United States." Accordingly, Lieutenant Kingston, Burgoyne's adjutant general, appeared at the appointed hour and delivered the following note from his commander: "After having fought you twice, Lieutenant-general Burgoyne has waited some days in his present position, determined to try a third conflict against any force you could bring against him. He is apprized of your superiority of numbers, and the disposition of your troops to impede his supplies, and render his retreat a scene of carnage on both sides. In this situation, he is impelled by humanity, and thinks himself justified by established principles and precedents of state and war, to spare the lives of brave men upon honorable terms. Should Major general Gates be inclined to treat upon that idea, General Burgoyne would propose a cessation of arms during the time necessary to communicate the preliminary terms by which, in any extremity, he and his army mean to abide."
General Gates had already prepared a schedule of terms upon which he was willing to treat. It enumerated the distresses of the British army, and declared that they could only be allowed to surrender as prisoners of war, and that they must lay down their arms in their camp. Burgoyne replied, with spirit, that he would not admit that the retreat of his army was cut off while they had arms in their hands, and that the degrading act of laying down their arms within their own camp would not be submitted to. The latter condition was waived, and in the afternoon General Gates ordered a. cessation of hostilities till sunset. Negotiations continued until the 16th, when every thing was agreed upon and adjusted, ready for the signatures of the contracting parties. This last act was to be performed on the morning of the 17th.
The substance of the "Convention between Lieutenant-general Burgoyne and Major general Gates," as the British commander superscribed it, was, 1st. That Burgoyne's troops were to march out of their camp with all the honors of war, the artillery to be moved to the verge of the Hudson, and there left, together with the soldiers' arms-the said arms to be piled by word of command from their own officers; 2d. That a free passage should be granted the troops to Great Britain, on condition of their not serving again during the war; 3d. That if any cartel should take place by which Burgoyne's army, or any part of it, should be exchanged, the foregoing article should be void as far as such exchange should extend; 4th. That the army should march to the neighborhood of Boston by the most expeditious and convenient route, and not be delayed when transports should arrive to receive them; 5th. That every care should be taken for the proper subsistence of the troops till they should be embarked; 6th. That all officers should retain their carriages, horses, bat-horses, &e., and their baggage, and be exempt from molestation or search; 7th. That on the march, and while the army should remain at Boston (the port selected for their embarkation), the officers should not be separated from their men; 8th. That all corps whatsoever, whether composed of sailors, bateaux-men, artificers, drivers, independent companies, or followers of the army, of whatever country they might be, should be included in the fullest sense and to the utmost extent of the articles, and comprehended in every respect as British subjects, whose general had capitulated for them;(1) 9th. That all Canadians and persons belonging to the Canadian establishment should be permitted a free return to Canada, should be con. ducted by the shortest route to the British posts on Lake George,. should be treated in all respects like the rest of the army, and should be bound by the same conditions not to serve during the war, unless exchanged; 10th. That passports should be immediately granted for three officers, to carry Burgoyne's dispatches to General Howe at Philadelphia, to Sir Guy Carleton in Canada, and to the government of Great Britain by way of New York; 11th. That all officers, during their stay in Boston, should be admitted to parole, and from
1 This was to afford protection to the loyalists or Tories.